Study links nanoparticles to altered blood vessel formation in embryos
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
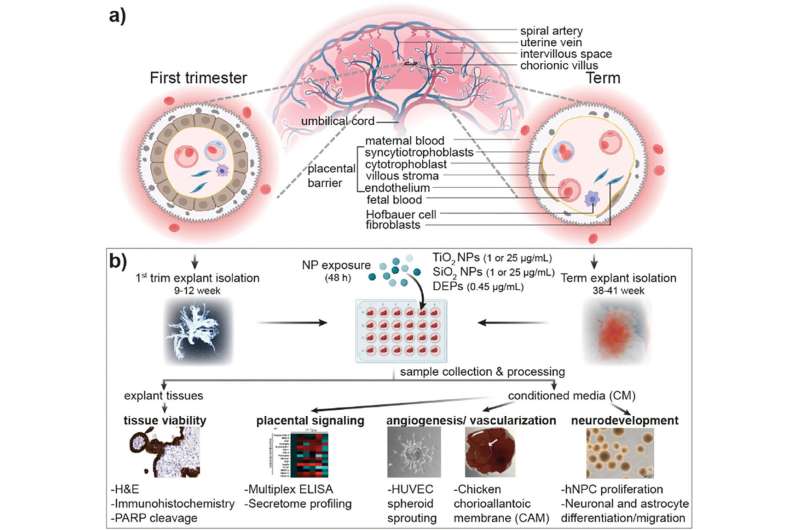
Human life begins with a single egg cell that grows into a human being with trillions of cells. To ensure that the highly complex development of tissues and organs is as protected as possible, the placental barrier keeps pathogens and foreign substances out. Tina Bürki and her team from Empa’s Particles-Biology Interactions laboratory in St. Gallen are investigating how this protective mechanism copes with nanoparticles.
The findings are published in the journal Advanced Science.
Nanoparticles are contained in a large number of products, but they are also produced during wear and tear as well as through combustion processes. «We absorb these substances from the environment via our food, cosmetics or the air we breathe,» explains Bürki.
Some of these nanoparticles are suspected of harming babies in the womb. Low birth weight, autism and respiratory diseases are among the possible consequences for the child.
Mysterious remote effect
It is still unclear how the nanoparticles affect the unborn child. «We already know that the placental barrier retains many nanoparticles or at least delays their transport to the embryo,» says Bürki. However, damage to the fetal tissue occurs, even if no particles have been detected in the fetus. The Empa team is now getting to the bottom of this long-range effect of nanoparticles.
Together with clinical partners from the Cantonal Hospital of St. Gallen and research partners from the University of Geneva, the Amsterdam University Medical Center and the Leibniz Institute for Environmental Medical Research in Düsseldorf, the team is investigating the consequences of common nanoparticles such as titanium dioxide or diesel soot on the function of the placenta and their indirect damage to embryonic development.
For this purpose, the team used fully functional human placentas that were made available after planned cesarean sections. «Human placental tissue is the only way to obtain meaningful results on the transport and effect of nanoparticles,» says the Empa researcher. «The structure, metabolism and interaction of maternal and fetal tissue are unique and species-specific.»
The experiments showed that nanoparticles in placental tissue disrupt the production of a large number of messenger substances. And it is these messengers that can trigger serious changes in embryonic development, such as disturbed blood vessel formation.
These effects can be visualized in laboratory models using chicken eggs. The blood vessels in the egg actually grow at an enormous speed and density to enable embryonic development. A dense network of fine blood vessels covers the inside of the eggshell.
The situation is strikingly different in eggs treated with the altered messenger substances from the nanoparticle-treated placenta: In the experiments, the blood vessel system was not as dense but rather coarse-meshed. «Nanoparticles apparently have an indirect effect on the child in the womb by inhibiting the formation of blood vessels via messenger substances,» says Tina Bürki.
Health consequences
The researchers are currently investigating the entirety of the messenger substances released by a nanoparticle-treated placenta, the so-called secretome. Uncontaminated, the interplay of hormones, inflammatory mediators and signaling substances for the formation of organ systems resembles a perfectly tuned orchestra.
It is already clear that the communication between the placenta and the unborn child is disrupted by the presence of nanoparticles and damages the formation of blood vessels. However, initial results show that the development of the nervous system does not appear to be affected.
Future analyses will show what other disorders the nanoparticles can trigger indirectly. «As the effects can have an impact on the health of the pregnant woman and the development of her child, these findings should be taken into account in the risk assessment of nanomaterials,» says the researcher.
The clinical partner, the Cantonal Hospital of St. Gallen, is also interested. As Thomas Rduch from the Women’s Clinic and also a Clinical Research Fellow at Empa puts it, «A healthy placenta is of utmost importance for the development of the child. Correct risk assessments of environmental pollution are therefore crucial for pregnant women.»
More information:
Battuja Dugershaw‐Kurzer et al, Nanoparticles Dysregulate the Human Placental Secretome with Consequences on Angiogenesis and Vascularization, Advanced Science (2024). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202401060
Provided by
Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology
Citation:
Study links nanoparticles to altered blood vessel formation in embryos (2024, June 6)
retrieved 16 June 2024
from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment